Underdetermined Linear Systems
Contents
18.3. Underdetermined Linear Systems#
The discussion in this section is primarily based on chapter 1 of [30].
Consider a matrix
Define an under-determined system of linear equations:
where
This system has
There are more unknowns than equations.
Let the columns of
Column space of
We know that
Clearly
Thus if
But, if
Let
Let
Let
Then
Hence
Thus the set
Example 18.2 (An under-determined system)
As a running example in this section,
we will consider a simple under-determined system
in
The system is specified by
and
with
where
or more simply
The solution space of this system is a line in
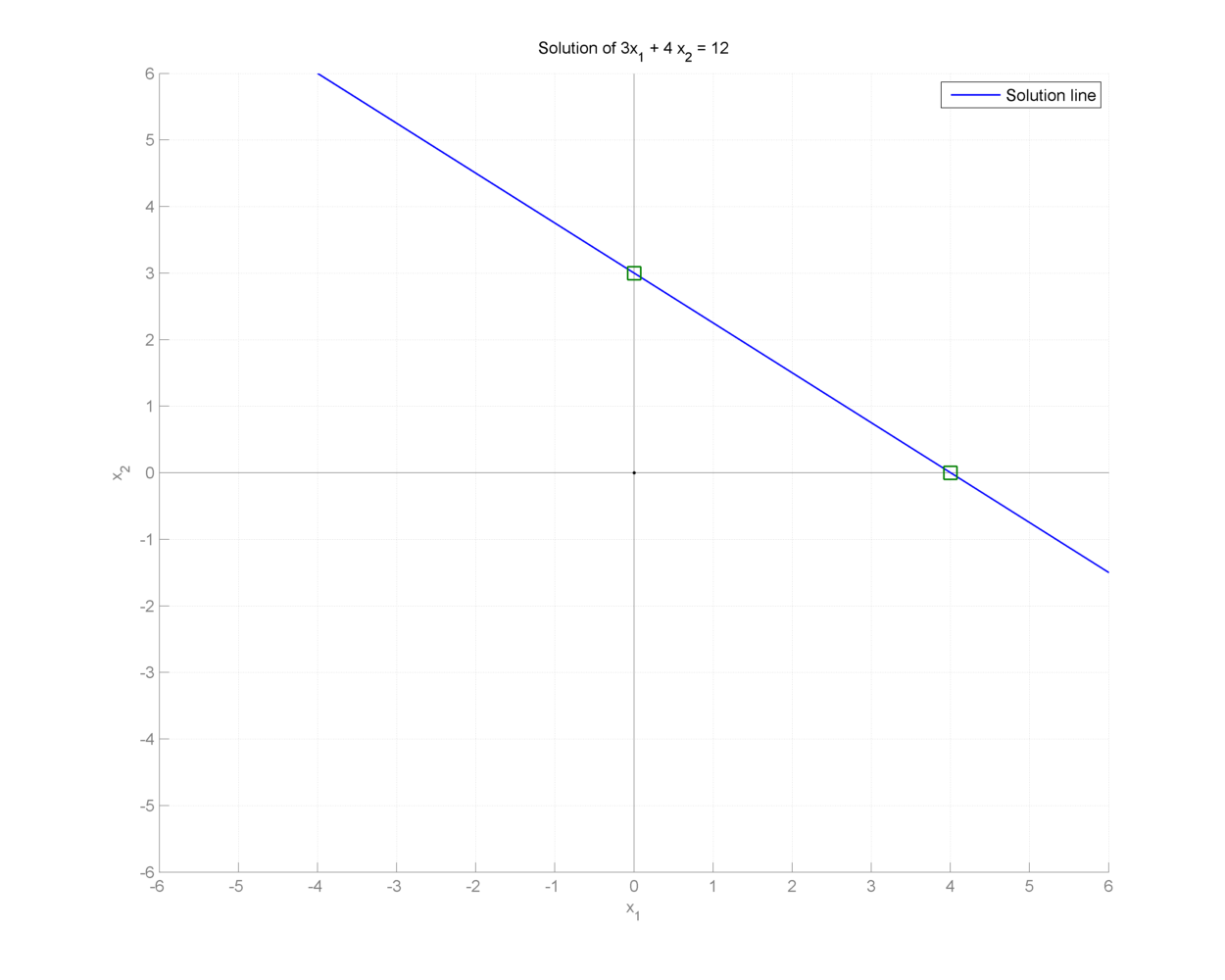
Fig. 18.1 An underdetermined system#
Specification of the under-determined system as above, doesn’t give us any reason to pick one particular point on the line as the preferred solution.
Two specific solutions are of interest
In both of these solutions, one component is 0, thus leading these solutions to be sparse.
It is easy to visualize sparsity in this simplified 2-dimensional setup but situation becomes more difficult when we are looking at high dimensional signal spaces. We need well defined criteria to promote sparse solutions.
18.3.1. Regularization#
Are all these solutions equivalent or can we say that one solution is better than the other in some sense? In order to suggest that some solution is better than other solutions, we need to define a criteria for comparing two solutions.
In optimization theory, this idea is known as regularization.
We define a cost function
Thus the goal of the optimization problem is to find a desired
We can write this optimization problem as
If
If
A variety of such cost function based criteria can be considered.
18.3.2.
One of the most common criteria is to choose a solution with the smallest
The problem can then be reformulated as an optimization problem
We can see that minimizing
Hence an equivalent formulation is
Example 18.3 (Minimum
We continue with our running example.
We can write
With this definition the squared
Minimizing
Since
This gives us
Thus the optimal
We note that the minimum
It is instructive to note that the
We can view this solution graphically by drawing
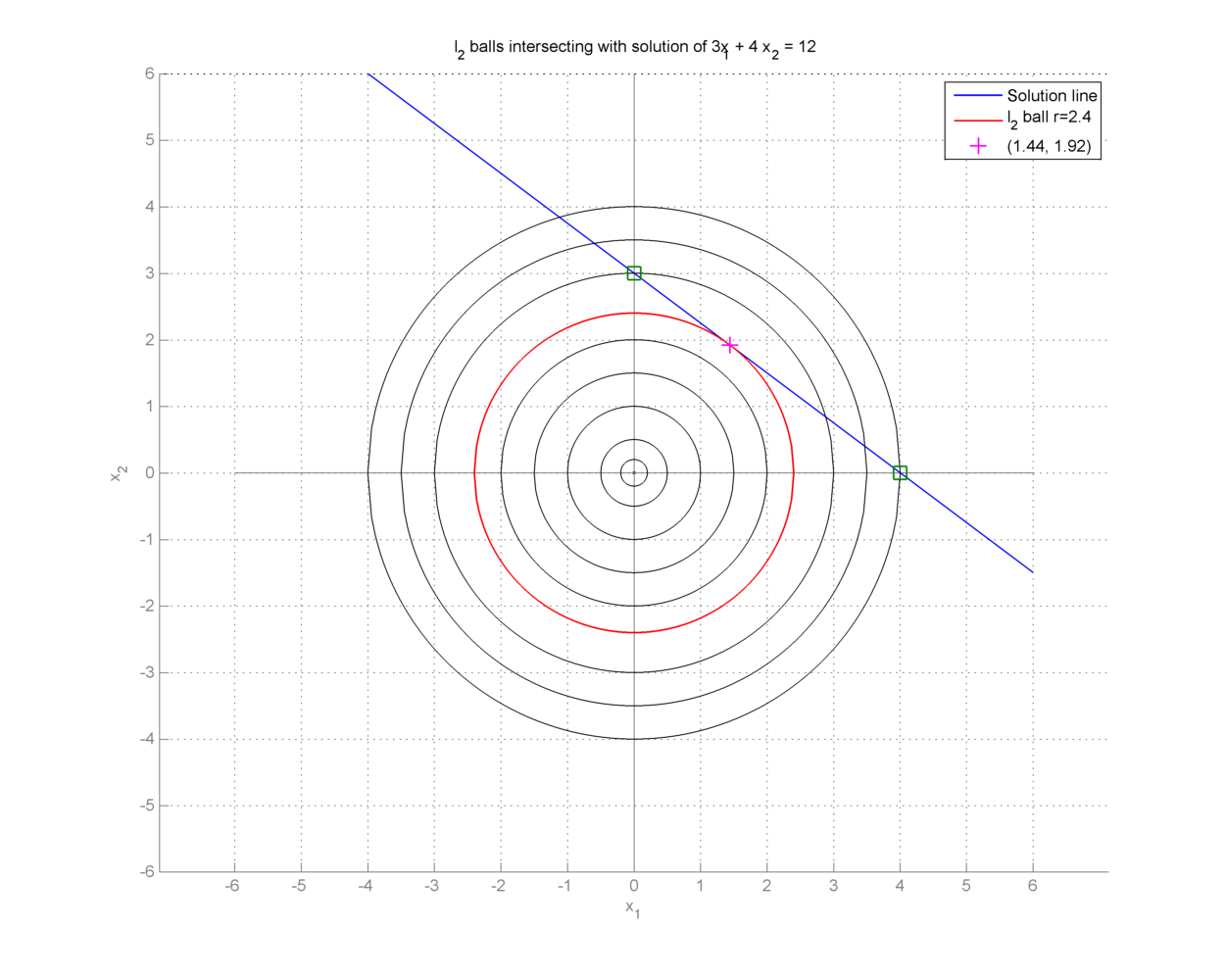
Fig. 18.2 Minimum
All other norm balls either don’t touch the solution line at all, or they cross it at exactly two points.
Remark 18.1 (Least squares via Lagrangian multipliers)
A formal solution to
We define the Lagrangian
with
Differentiating
By equating the derivative to
Plugging this solution back into the constraint
In above we are implicitly assuming that
Putting
We would like to mention that there are several iterative approaches to solve the
The beauty of
18.3.2.1. Convexity#
Convex optimization problems have a unique feature that it is possible to find the global optimal solution if such a solution exists.
The solution space
We recall that all
and
In the following section we will attempt to find a unique solution to our
optimization problem (18.1) using
18.3.3.
In this subsection we will restrict our attention to the
Euclidean space case where
We choose our cost function
Example 18.4 (Minimum
We continue with our running example.
we can view this solution graphically by drawing
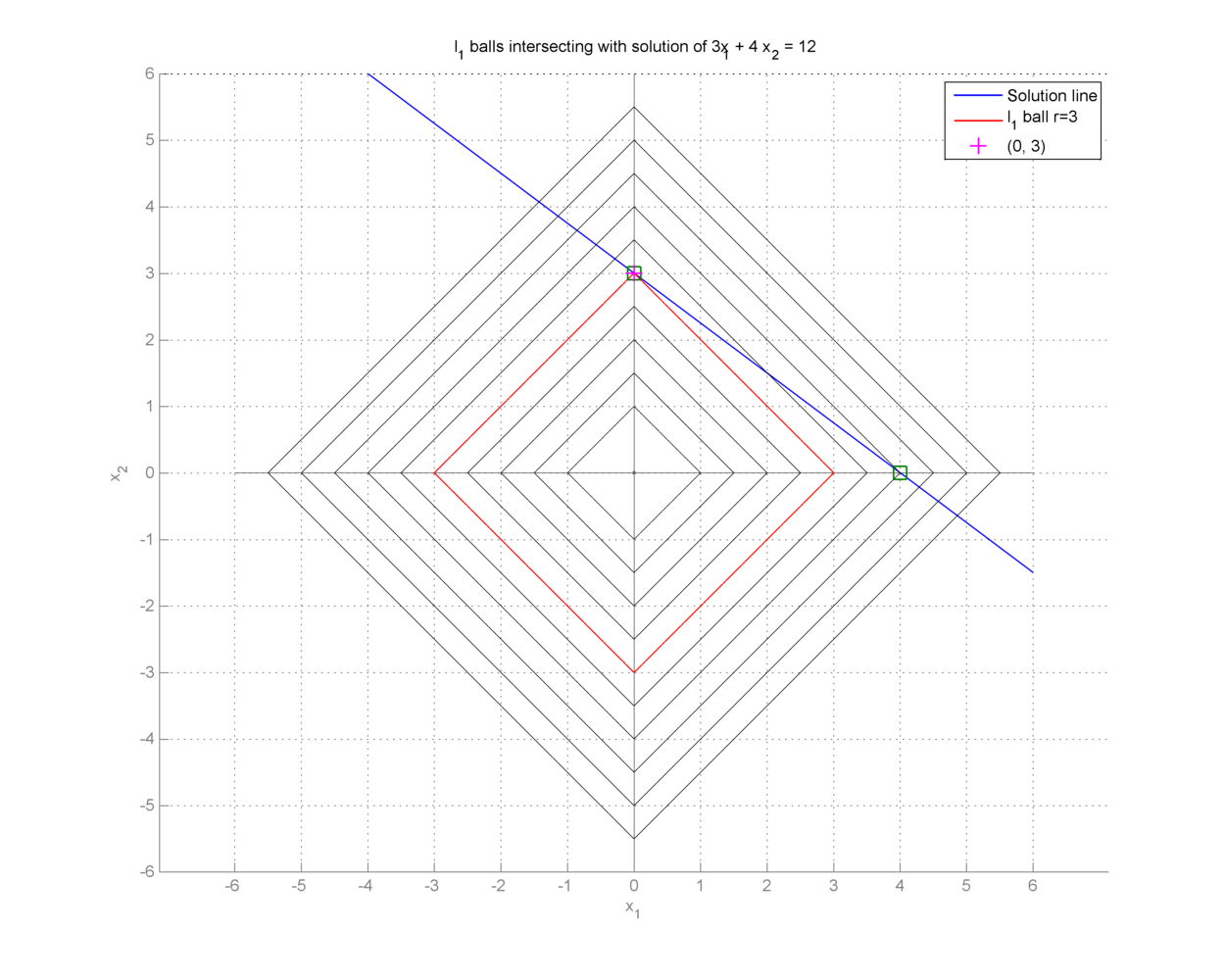
Fig. 18.3 Minimum
As we can see from the figure the minimum
It is interesting to note that
It is time to have a closer look at our cost function
Example 18.5 (
Consider again
Hence for any
Thus,
As an example consider the under-determined system
We can easily visualize that the solution line will pass through points
Moreover, it will be clearly parallel with
This gives us infinitely possible solutions to the minimization problem (18.3).
We can still observe that
these solutions are gathered in a small line segment that is bounded (a bounded convex set) and
There exist two solutions
For the
these solutions are gathered in a set that is bounded and convex, and
among these solutions, there exists at least one solution with at most
Theorem 18.1 (Existence of a sparse solution for
Let
Proof. We have the following facts
Since
We proceed as follows.
Let
Consider the
Since
Thus there exists a nonzero vector
Note that since we are only considering those columns of
Consider a new vector
where
such an
Note that
Clearly
Thus
But since
Now look at
In this region,
If we define
Since the sign patterns don’t change, hence
Thus
The quantity
The inequality
This is possible only when inequality is in fact an equality.
This implies that the addition / subtraction of
Thus,
This can happen only if
We now wish to tune
We choose
Clearly for the corresponding
the
Thus, we have got a new optimal solution with
It is possible that more than 1 entries get zeroed during this operation.
We can repeat this procedure till we are left with
Beyond this we may not proceed since
We thus note that
18.3.4.
We now show that (18.3) in
Recalling the problem:
Let us write
Example 18.6 (
Let
Then
And
Clearly
We note here that by definition
i.e., support of
We now construct a vector
We can now verify that
Also
where
Hence the optimization problem (18.3) can be recast as
This optimization problem has the classic Linear Programming structure since the objective function is affine as well as constraints are affine.
Remark 18.2 (Justification for the equivalence of the linear program)
Let
In order to show that the two optimization problems are equivalent, we need
to verify that our assumption about the decomposition of
Since
If support of
And if they overlap then
Now for the sake of contradiction, let us assume that support of
Let
Since
Without loss of generality let us assume that
In the equality constraint
both of these coefficients multiply the same column of
Now if we replace the two entries in
and
to obtain an new vector
Also the nonnegativity constraint
is satisfied for
This means that
On the other hand the objective function
This contradicts our assumption that
Hence for the optimal solution of (18.4) we must have
Thus
is indeed the desired solution for the optimization problem (18.3).